Developments / New technologies
ENERGY AND ECO-EFFICIENT MECHANOCHEMICAL SYNTHESIS OF NANO-LiFePO4/С FOR LITHIUM-ION BATTERIES
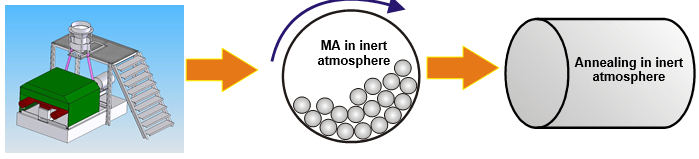
Energy and eco-efficient mechanochemical method of synthesis of nanocomposite cathode material LiFePO4/С with grain size ~ 50 nm has been developed in the Institute of Solid State Chemistry and Mechanochemistry of Siberian Branch of Russian Academy of Sciences.
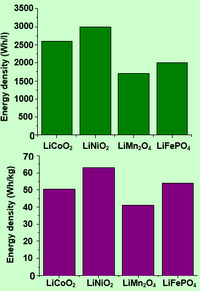
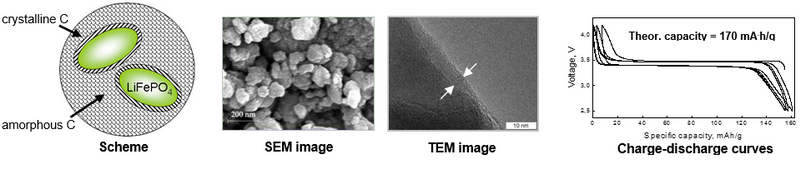
Cathode material LiFePO4/C is characterized by high discharge voltage (3.4 V vs. Li/Li+), the presence of plateau on charge-discharge curves and a high theoretical capacity (170 mA∙h/g), which can be achieved in practice.
LiFePO4 is low-cost, nontoxic, structurally and chemically stable when charging at increased temperatures; its electrochemical features are comparable with those of well-known cathode materials.
Nanocomposite prepared by mechanical activation (MA) - the grains of LiFePO4, surface-modified by crystalline carbon embedded into the matrix of amorphous carbon – overcomes the main disadvantage of LiFePO4 – low electronic conductivity (10-9 S/cm) and ensures high-rate capability and high discharge capacity 150-160 mA∙h/g, close to the theoretical one.
Method of synthesis LiFePO4/С:
Characteristics of mechanonanocomposite LiFePO4/С:
The advantages of the method:

- preparation of fine LiFePO4 particles;
- formation of uniform nano-sized conducting carbon coating;
- combination of the synthesis and the coating stages;
- low time and energy inputs;
- echo-efficiency (the absence of wastes (opposite to solution methods)
LiFePO4 is a promising material to be used in hybrid and electro-vehicles, where the cost and safety are of great importance.
Contact us:
Institute of Solid State Chemistry and Mechanochemistry SB RAS
Kutateladze str., 18 Novosibirsk, 630128 Russia
Phone: +7(383)332-53-44
Fax: +7(383)332-28-47
E-mail: root@solid.nsc.ru